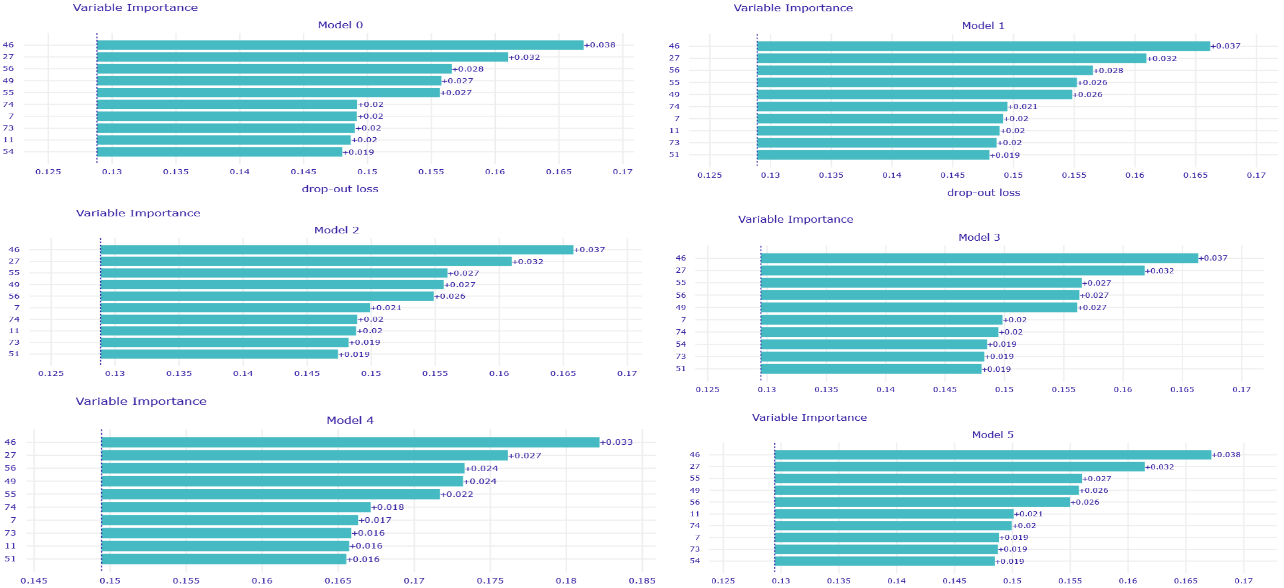
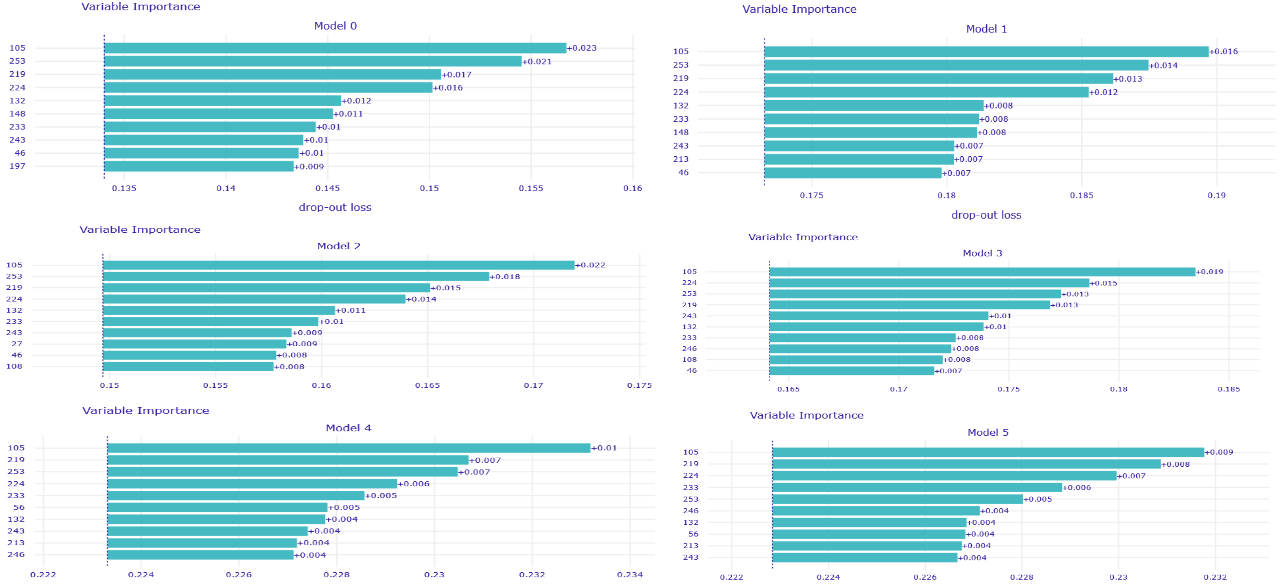
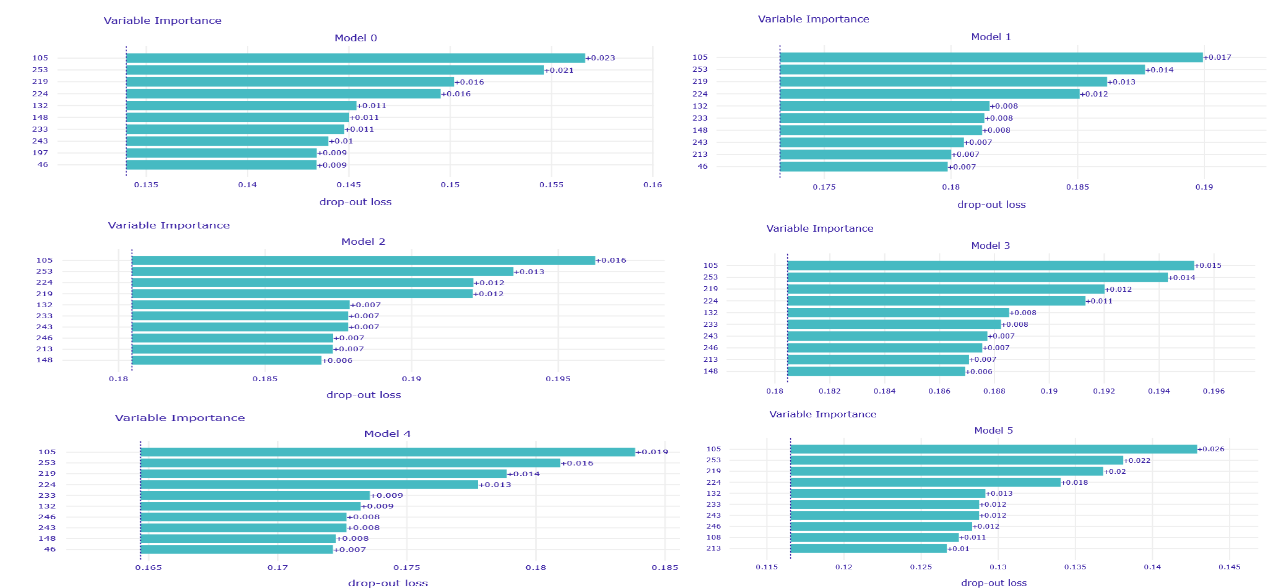
This time, voting experts had worse results than the best model/models when given larger set of variables - W48.
Abadi, M., Agarwal, A., Barham, P., Brevdo, E., Chen, Z., Citro, C., et al., et al. (2015).
TensorFlow: Large-Scale Machine Learning on Heterogeneous Systems.
USENIX conference on Operating Systems Design and Implementation.
https://dl.acm.org/doi/10.5555/3026877.3026899
Ahmad, M. W., Mourshed, M., & Rezgui, Y. (2017).
Trees vs Neurons: Comparison between random forest and ANN for high-resolution prediction of building energy consumption.
Energy and Buildings,
147, 77--89.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enbuild.2017.04.038
Aivodji, U., Arai, H., Fortineau, O., Gambs, S., Hara, S., & Tapp, A. (2019). Fairwashing: The risk of rationalization. In K. Chaudhuri & R. Salakhutdinov (Eds.),
Proceedings of the 36th international conference on machine learning (Vol. 97, pp. 161–170). PMLR.
http://proceedings.mlr.press/v97/aivodji19a.html
Andriawan, Z. A., Purnama, S. R., Darmawan, A. S., Ricko, Wibowo, A., Sugiharto, A., & Wijayanto, F. (2020). Prediction of hotel booking cancellation using CRISP-DM. In
2020 4th international conference on informatics and computational sciences (ICICoS) (pp. 1–6).
https://doi.org/10.1109/ICICoS51170.2020.9299011
Anthimopoulos, M., Christodoulidis, S., Ebner, L., Geiser, T., Christe, A., & Mougiakakou, S. (2019). Semantic segmentation of pathological lung tissue with dilated fully convolutional networks.
IEEE Journal of Biomedical and Health Informatics,
23(2), 714–722.
https://doi.org/10.1109/JBHI.2018.2818620
Antonio, N., de Almeida, A., & Nunes, L. (2017). Predicting hotel booking cancellations to decrease uncertainty and increase revenue.
Tourism & Management Studies,
13(2), 25–39.
https://doi.org/10.18089/tms.2017.13203
Antonio, N., de Almeida, A., & Nunes, L. (2019a). An automated machine learning based decision support system to predict hotel booking cancellations.
Data Science Journal,
18(1), 1–20.
https://doi.org/10.5334/dsj-2019-032
Antonio, N., de Almeida, A., & Nunes, L. (2019b). Hotel booking demand datasets.
Data in Brief,
22, 41–49.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dib.2018.11.126
Apley, D. W., & Zhu, J. (2020).
Visualizing the effects of predictor variables in black box supervised learning models.
Journal of the Royal Statistical Society Series B,
82(4), 1059–1086.
https://doi.org/10.1111/rssb.12377
Arik, S. O., & Pfister, T. (2021).
TabNet: Attentive Interpretable Tabular Learning.
AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence (AAAI).
https://arxiv.org/abs/1908.07442
Arsad, P. M., Buniyamin, N., & Manan, J. A. (2013).
Prediction of engineering students’ academic performance using Artificial Neural Network and Linear Regression: A comparison.
ICEED.
https://doi.org/10.1109/iceed.2013.6908300
Asadi-Aghbolaghi, M., Azad, R., Fathy, M., & Escalera, S. (2020). Multi-level context gating of embedded collective knowledge for medical image segmentation.
https://arxiv.org/abs/2003.05056
Azad, R., Asadi-Aghbolaghi, M., Fathy, M., & Escalera, S. (2019). Bi-directional ConvLSTM u-net with densley connected convolutions. In
2019 IEEE/CVF international conference on computer vision workshop (ICCVW) (pp. 406–415).
https://doi.org/10.1109/ICCVW.2019.00052
Baker, M. (2016). Reproducibility crisis. Nature, 533(26), 353–66.
Baniecki, H., Kretowicz, W., Piatyszek, P., Wisniewski, J., & Biecek, P. (2020a).
dalex: Responsible Machine Learning with Interactive Explainability and Fairness in Python.
arXiv:2012.14406.
https://arxiv.org/abs/2012.14406
Baniecki, H., Kretowicz, W., Piatyszek, P., Wisniewski, J., & Biecek, P. (2020b).
dalex: Responsible Machine Learning with Interactive Explainability and Fairness in Python.
arXiv:2012.14406.
https://arxiv.org/abs/2012.14406
Barda, N., Riesel, D., Akriv, A., Levy, J., Finkel, U., Yona, G., et al. (2020).
Developing a COVID-19 mortality risk prediction model when individual-level data are not available.
Nature Communications,
11.
https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-020-18297-9
Barish, M., Bolourani, S., Lau, L. F., Shah, S., & Zanos, T. P. (2020).
External validation demonstrates limited clinical utility of the interpretable mortality prediction model for patients with COVID-19.
Nature Machine Intelligence,
3, 25–27.
https://doi.org/10.1038/s42256-020-00254-2
Barish, M., Bolourani, S., Lau, L. F., Shah, S., & Zanos, T. P. (2021).
External validation demonstrates limited clinical utility of the interpretable mortality prediction model for patients with COVID-19.
Nature Machine Intelligence,
3(1), 25–27.
https://doi.org/10.1038/s42256-020-00254-2
Barredo Arrieta, A., Díaz-Rodríguez, N., Del Ser, J., Bennetot, A., Tabik, S., Barbado, A., et al. (2020c).
Explainable Artificial Intelligence (XAI): Concepts, taxonomies, opportunities and challenges toward responsible AI.
Information Fusion,
58, 82–115.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.inffus.2019.12.012
Barredo Arrieta, A., Díaz-Rodríguez, N., Del Ser, J., Bennetot, A., Tabik, S., Barbado, A., et al. (2020b). Explainable artificial intelligence (XAI): Concepts, taxonomies, opportunities and challenges toward responsible AI.
Information Fusion,
58, 82–115.
http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1566253519308103
Barredo Arrieta, A., Díaz-Rodríguez, N., Del Ser, J., Bennetot, A., Tabik, S., Barbado, A., et al. (2020a). Explainable artificial intelligence (XAI): Concepts, taxonomies, opportunities and challenges toward responsible AI.
Information Fusion,
58, 82–115.
http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1566253519308103
Barsoum, E., Zhang, C., Ferrer, C. C., & Zhang, Z. (2016). Training deep networks for facial expression recognition with crowd-sourced label distribution. In
Proceedings of the 18th ACM international conference on multimodal interaction (pp. 279–283). New York, NY, USA: Association for Computing Machinery.
https://doi.org/10.1145/2993148.2993165
Belke, A., & Keil, J. (2017). Fundamental determinants of real estate prices: A panel study of german regions, (731). Ruhr Economic Papers.
https://doi.org/10.4419/86788851
Bello-Chavolla, O. Y., Bahena-López, J. P., Antonio-Villa, N. E., Vargas-Vázquez, A., González-Díaz, A., Márquez-Salinas, A., et al. (2020).
Predicting Mortality Due to SARS-CoV-2: A Mechanistic Score Relating Obesity and Diabetes to COVID-19 Outcomes in Mexico.
The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism,
105, 2752--2761.
https://doi.org/10.1210/clinem/dgaa346
Berk, R., Heidari, H., Jabbari, S., Kearns, M., & Roth, A. (2017).
Fairness in Criminal Justice Risk Assessments: The State of the Art.
Sociological Methods & Research.
https://doi.org/10.1177/0049124118782533
Biecek, P. (2018b).
DALEX: Explainers for Complex Predictive Models in R.
Journal of Machine Learning Research,
19(84), 1–5.
https://jmlr.org/papers/v19/18-416.html
Biecek, P. (2018a).
DALEX: Explainers for Complex Predictive Models in R.
Journal of Machine Learning Research,
19(84), 1–5.
http://jmlr.org/papers/v19/18-416.html
Biecek, P., & Burzykowski, T. (2021).
Explanatory Model Analysis. Chapman; Hall/CRC, New York.
https://pbiecek.github.io/ema/
Bird, S., Dudík, M., Edgar, R., Horn, B., Lutz, R., Milan, V., et al. (2020).
Fairlearn: A toolkit for assessing and improving fairness in AI (No. MSR-TR-2020-32). Microsoft.
https://www.microsoft.com/en-us/research/publication/fairlearn-a-toolkit-for-assessing-and-improving-fairness-in-ai/
Bisong, E. (2019). Google colaboratory. In Building machine learning and deep learning models on google cloud platform (pp. 59–64). Springer.
Bradley, A. P. (1997). The use of the area under the ROC curve in the evaluation of machine learning algorithms.
Pattern Recogn.,
30(7), 1145–1159.
https://doi.org/10.1016/S0031-3203(96)00142-2
Breiman, L. (1999). Random forests. UC Berkeley TR567.
Breiman, L. et al. (2001). Statistical modeling: The two cultures (with comments and a rejoinder by the author). Statistical science, 16(3), 199–231.
Can, A. (1990). The measurement of neighborhood dynamics in urban house prices.
Economic Geography,
66(3), 254–272.
https://doi.org/10.2307/143400
Cao, Y., Liu, X., Xiong, L., & Cai, K. (2020).
Imaging and clinical features of patients with 2019 novel coronavirus SARS-CoV-2: A systematic review and meta-analysis.
Journal of Medical Virology,
92(9), 1449–1459.
https://doi.org/10.1002/jmv.25822
Casadevall, A., & Fang, F. C. (2010). Reproducible science.
Infection and Immunity,
78(12), 4972–4975.
https://doi.org/10.1128/IAI.00908-10
Chen, T., & Guestrin, C. (2016).
XGBoost: A Scalable Tree Boosting System.
KDD. https://doi.org/
https://doi.org/10.1145/2939672.2939785
Chollet, F. (2017). Deep learning with python. Manning.
Chouldechova, A. (2016).
Fair Prediction with Disparate Impact: A Study of Bias in Recidivism Prediction Instruments.
Big Data,
5.
https://doi.org/10.1089/big.2016.0047
Chowdhury, M. E. H., Rahman, T., Khandakar, A., Mazhar, R., Kadir, M. A., Mahbub, Z. B., et al. (2020). Can AI help in screening viral and COVID-19 pneumonia?
IEEE Access,
8, 132665–132676.
https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2020.3010287
Christe, A. A. M. D., Andreas MD∗; Peters. (2019). Computer-aided diagnosis of pulmonary fibrosis using deep learning and CT images.
Investigative Radiology,
54, 627–632.
https://doi.org/10.1097/RLI.0000000000000574
Chu, X., Ilyas, I. F., Krishnan, S., & Wang, J. (2016). Data cleaning: Overview and emerging challenges. In Proceedings of the 2016 international conference on management of data (pp. 2201–2206).
Clark, K., Vendt, B., Smith, K., Freymann, J., Kirby, J., Koppel, P., et al. (2013). The cancer imaging archive (TCIA): Maintaining and operating a public information repository.
Journal of Digital Imaging,
26(6), 1045–1057.
https://doi.org/10.1007/s10278-013-9622-7
Code of Federal Regulations. (1978). SECTION 4D, UNIFORM GUIDELINES ON EMPLOYEE SELECTION PROCEDURES (1978).
https://www.govinfo.gov/content/pkg/CFR-2014-title29-vol4/xml/CFR-2014-title29-vol4-part1607.xml
Cohen, J. P., Morrison, P., Dao, L., Roth, K., Duong, T. Q., & Ghassemi, M. (2020). COVID-19 image data collection: Prospective predictions are the future.
arXiv 2006.11988.
https://github.com/ieee8023/covid-chestxray-dataset
Computing Machinery, A. for. (2018). Artifact review and badging.
https://www.acm.org/publications/policies/artifact-review badging
Conway, J. (2018, January).
Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning : Current Applications in Real Estate (PhD thesis). Retrieved from
https://dspace.mit.edu/bitstream/handle/1721.1/120609/1088413444-MIT.pdf
Corbett-Davies, S., Pierson, E., Feller, A., Goel, S., & Huq, A. (2017).
Algorithmic Decision Making and the Cost of Fairness.
https://doi.org/10.1145/3097983.3098095
Das, S., Cashman, D., Chang, R., & Endert, A. (2019). BEAMES: Interactive multimodel steering, selection, and inspection for regression tasks.
IEEE Computer Graphics and Applications,
39(5), 20–32.
https://doi.org/10.1109/MCG.2019.2922592
Davis, J., & Goadrich, M. (2006). The relationship between precision-recall and ROC curves. In
Proceedings of the 23rd international conference on machine learning (pp. 233–240). New York, NY, USA: Association for Computing Machinery.
https://doi.org/10.1145/1143844.1143874
Dong, J., & Rudin, C. (2020). Exploring the cloud of variable importance for the set of all good models. Nature Machine Intelligence, 2(12), 810–824.
Du, X., Cai, Y., Wang, S., & Zhang, L. (2016). Overview of deep learning. In 2016 31st youth academic annual conference of chinese association of automation (YAC) (pp. 159–164). IEEE.
Dubin, R. A. (1998). Predicting house prices using multiple listings data.
The Journal of Real Estate Finance and Economics.
https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1007751112669
Dupuis, C., De Montmollin, E., Neuville, M., Mourvillier, B., Ruckly, S., & Timsit, J. F. (2021).
Limited applicability of a COVID-19 specific mortality prediction rule to the intensive care setting.
Nature Machine Intelligence,
3(1), 20–22.
https://doi.org/10.1038/s42256-020-00252-4
Dwork, C., Hardt, M., Pitassi, T., Reingold, O., & Zemel, R. (2012). Fairness through awareness.
ITCS.
https://doi.org/10.1145/2090236.2090255
Falk, M., & Vieru, M. (2018). Modelling the cancellation behaviour of hotel guests.
International Journal of Contemporary Hospitality Management,
30(10), 3100–3116.
https://doi.org/10.1108/ijchm-08-2017-0509
Fan, C., Cui, Z., & Zhong, X. (2018). House prices prediction with machine learning algorithms. In
Proceedings of the 2018 10th international conference on machine learning and computing (pp. 6–10). New York, NY, USA: Association for Computing Machinery.
https://doi.org/10.1145/3195106.3195133
Fawcett, T. (2006). An introduction to ROC analysis.
Pattern Recognition Letters,
27(8), 861–874. https://doi.org/
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.patrec.2005.10.010
Finlayson, S. G., Chung, H. W., Kohane, I. S., & Beam, A. L. (2018). Adversarial attacks against medical deep learning systems. arXiv preprint arXiv:1804.05296.
Fisher, A., Rudin, C., & Dominici, F. (2019a). All models are wrong, but many are useful: Learning a variable’s importance by studying an entire class of prediction models simultaneously.
Journal of Machine Learning Research,
20(177), 1–81.
http://jmlr.org/papers/v20/18-760.html
Fisher, A., Rudin, C., & Dominici, F. (2019b).
All Models are Wrong, but Many are Useful: Learning a Variable’s Importance by Studying an Entire Class of Prediction Models Simultaneously.
Journal of Machine Learning Research,
20(177), 1–81.
http://jmlr.org/papers/v20/18-760.html
Fisher, A., Rudin, C., & Dominici, F. (2019c). All models are wrong, but many are useful: Learning a variable’s importance by studying an entire class of prediction models simultaneously. Journal of Machine Learning Research, 20(177), 1–81.
Friedman, J. H. (2000). Greedy function approximation: A gradient boosting machine. Annals of Statistics, 29, 1189–1232.
Ge, X., Runeson, G., & Lam, K. C. (2021). Forecasting hong kong housing prices: An artificial neural network approach.
Géron, A. (2017). Hands-on machine learning with scikit-learn and TensorFlow : Concepts, tools, and techniques to build intelligent systems. O’Reilly Media.
Ghysels, E., Plazzi, A., Valkanov, R., & Torous, W. (2013). Chapter 9 - forecasting real estate prices,
2, 509–580. https://doi.org/
https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-444-53683-9.00009-8
Glauner, P. (2021). An assessment of the AI regulation proposed by the european commission.
https://arxiv.org/abs/2105.15133
GOLDNER, M. C., ZAMORA, M. C., DI LEO LIRA, P., GIANNINOTO, H., & BANDONI, A. (2009). EFFECT OF ETHANOL LEVEL IN THE PERCEPTION OF AROMA ATTRIBUTES AND THE DETECTION OF VOLATILE COMPOUNDS IN RED WINE. Journal of sensory studies, 24(2), 243–257.
Goldstein, A., Kapelner, A., Bleich, J., & Pitkin, E. (2014). Peeking inside the black box: Visualizing statistical learning with plots of individual conditional expectation.
Goodman, B., & Flaxman, S. (2017). European union regulations on algorithmic decision-making and a
“right to explanation.” AI Magazine,
38(3), 50–57.
https://doi.org/10.1609/aimag.v38i3.2741
Gosiewska, A., & Biecek, P. (2019).
Do Not Trust Additive Explanations.
arXiv.
https://arxiv.org/abs/1903.11420v3
Goyal, S. (2020, November). Credit card customers.
Kaggle.
https://www.kaggle.com/sakshigoyal7/credit-card-customers
Hanley, J. A. (2014).
Receiver Operating Characteristic (ROC) Curves.
Wiley StatsRef: Statistics Reference Online.
https://doi.org/10.1002/9781118445112.stat05255
Hardt, M., Price, E., Price, E., & Srebro, N. (2016).
Equality of Opportunity in Supervised Learning.
NeurIPS.
https://papers.nips.cc/paper/2016/hash/9d2682367c3935defcb1f9e247a97c0d-Abstract.html
Heyman, A., & Sommervoll, D. (2019). House prices and relative location.
Cities,
95, 102373.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cities.2019.06.004
Jordão, A. M., Vilela, A., & Cosme, F. (2015). From sugar of grape to alcohol of wine: Sensorial impact of alcohol in wine.
Beverages,
1(4), 292–310.
https://doi.org/10.3390/beverages1040292
Karim, M. R., Döhmen, T., Rebholz-Schuhmann, D., Decker, S., Cochez, M., & Beyan, O. (2020). DeepCOVIDExplainer: Explainable COVID-19 diagnosis from chest x-ray images. IEEE.
https://doi.org/10.1109/BIBM49941.2020.9313304
Kaushal, A., Altman, R., & Langlotz, C. (2020).
Health Care AI Systems Are Biased.
Scientific American.
https://www.scientificamerican.com/article/health-care-ai-systems-are-biased
Klambauer, G., Unterthiner, T., Mayr, A., & Hochreiter, S. (2017).
Self-Normalizing Neural Networks.
arXiv:1706.02515.
https://arxiv.org/abs/1706.02515
Komisarczyk, Konrad and Maksymiuk, Szymon and Koźmiński, Paweł and Biecek, Przemysław. (2020).
treeshap: Fast SHAP values computation for ensemble models.
R package.
https://github.com/ModelOriented/treeshap
Kowsari, K., Brown, D. E., Heidarysafa, M., Jafari Meimandi, K., Gerber, M. S. and, & Barnes, L. E. (2017). HDLTex: Hierarchical deep learning for text classification. In Machine learning and applications (ICMLA), 2017 16th IEEE international conference on. IEEE.
Kowsari, K., Heidarysafa, M., Brown, D. E., Meimandi, K. J., & Barnes, L. E. (2018). Rmdl: Random multimodel deep learning for classification. In Proceedings of the 2nd international conference on information system and data mining (pp. 19–28).
Law, S. (2017). Defining street-based local area and measuring its effect on house price using a hedonic price approach: The case study of metropolitan london.
Cities,
60, 166–179.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cities.2016.08.008
Li, X., Ge, P., Zhu, J., Li, H., Graham, J., Singer, A., et al. (2020).
Deep learning prediction of likelihood of ICU admission and mortality in COVID-19 patients using clinical variables.
PeerJ,
8.
https://peerj.com/articles/10337/
Liu, C., Gao, C., Xia, X., Lo, D., Grundy, J., & Yang, X. (2020). On the replicability and reproducibility of deep learning in software engineering.
https://arxiv.org/abs/2006.14244
Loyola-González, O. (2019). Black-box vs. White-box: Understanding their advantages and weaknesses from a practical point of view.
IEEE Access,
7, 154096–154113.
https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2949286
Łukasz Rączkowski, J. Z., Marcin Możejko. (2019). ARA: Accurate, reliable and active histopathological image classification framework with bayesian deep learning.
Springer Nature,
14, 1–11.
https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-019-50587-1
Lundberg, Scott M., Erion, G. G., & Lee, S.-I. (2019).
Consistent Individualized Feature Attribution for Tree Ensembles.
ICML Workshop.
https://arxiv.org/abs/1802.03888
Lundberg, Scott M., & Lee, S.-I. (2017). A unified approach to interpreting model predictions. In I. Guyon, U. V. Luxburg, S. Bengio, H. Wallach, R. Fergus, S. Vishwanathan, & R. Garnett (Eds.),
Advances in neural information processing systems 30 (pp. 4765–4774). Montreal: Curran Associates.
http://papers.nips.cc/paper/7062-a-unified-approach-to-interpreting-model-predictions.pdf
Ma, X., Ng, M., Xu, S., Xu, Z., Qiu, H., Liu, Y., et al. (2020).
Development and validation of prognosis model of mortality risk in patients with COVID-19.
Epidemiology and Infection,
148.
http://doi.org/10.1017/S0950268820001727
Maksymiuk, S., Gosiewska, A., & Biecek, P. (2020). Landscape of r packages for eXplainable artificial intelligence.
arXiv.
https://arxiv.org/abs/2009.13248
Maksymiuk, S., Gosiewska, A., & Biecek, P. (2021). Landscape of r packages for eXplainable artificial intelligence.
https://arxiv.org/abs/2009.13248
Mendez, D., Graziotin, D., Wagner, S., & Seibold, H. (2020). Open science in software engineering.
Contemporary Empirical Methods in Software Engineering, 477–501.
https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-32489-6_17
Meyer, D., Dimitriadou, E., Hornik, K., Weingessel, A., Leisch, F., Chang, C.-C., & Lin, C.-C. (2021).
e1071: Misc Functions of the Department of Statistics, Probability Theory Group.
R package.
https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=e1071
Molnar, C. (2019).
Interpretable Machine Learning: A Guide for Making Black Box Models Explainable.
https://christophm.github.io/interpretable-ml-book
Neff, T., Payer, C., Stern, D., & Urschler, M. (2017). Generative adversarial network based synthesis for supervised medical image segmentation. In Proc. OAGM and ARW joint workshop.
Oktay, O., Schlemper, J., Folgoc, L. L., Lee, M., Heinrich, M., Misawa, K., et al., et al. (2018). Attention u-net: Learning where to look for the pancreas. arXiv preprint arXiv:1804.03999.
Pace, R. K., & Barry, R. (1997). Sparse spatial autoregressions. Statistics & Probability Letters, 33(3), 291–297.
Park, B., & Bae, J. (2015).
Using machine learning algorithms for housing price prediction: The case of Fairfax County, Virginia housing data.
Expert Systems with Applications,
42.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eswa.2014.11.040
Pedregosa, F., Varoquaux, G., Gramfort, A., Michel, V., Thirion, B., Grisel, O., et al. (2011a). Scikit-learn: Machine learning in Python. Journal of Machine Learning Research, 12, 2825–2830.
Pedregosa, F., Varoquaux, G., Gramfort, A., Michel, V., Thirion, B., Grisel, O., et al. (2011b). Scikit-learn: Machine Learning in Python. Journal of Machine Learning Research, 12, 2825–2830.
Pekala, K., Woznica, K., & Biecek, P. (2021). Triplot: Model agnostic measures and visualisations for variable importance in predictive models that take into account the hierarchical correlation structure.
CoRR,
abs/2104.03403.
https://arxiv.org/abs/2104.03403
Peng, Z., Huang, Q., & Han, Y. (2019). Model research on forecast of second-hand house price in chengdu based on XGboost algorithm, 168–172.
https://doi.org/10.1109/ICAIT.2019.8935894
Pineau, J., Vincent-Lamarre, P., Sinha, K., Larivière, V., Beygelzimer, A., d’Alché-Buc, F., et al. (2020). Improving reproducibility in machine learning research
(A report from the NeurIPS 2019 reproducibility program).
CoRR,
abs/2003.12206.
https://arxiv.org/abs/2003.12206
Quanjel, M. J. R., Holten, T. C. van, Gunst-van der Vliet, P. C., Wielaard, J., Karakaya, B., Söhne, M., et al. (2021). Replication of a mortality prediction model in dutch patients with COVID-19.
Nature Machine Intelligence,
3(1), 23–24.
https://doi.org/10.1038/s42256-020-00253-3
Quanjel, M. J. R., Holten, T. C. van, Vliet, P. C. G. der, Wielaard, J., Karakaya, B., Söhne, M., et al. (2021).
Replication of a mortality prediction model in Dutch patients with COVID-19.
Nature Machine Intelligence,
3, 23–24.
https://doi.org/10.1038/s42256-020-00253-3
R Core Team. (2018).
R: A language and environment for statistical computing. Vienna, Austria: R Foundation for Statistical Computing.
https://www.R-project.org/
Raghavan, V., Bollmann, P., & Jung, G. S. (1989). A critical investigation of recall and precision as measures of retrieval system performance.
ACM Trans. Inf. Syst.,
7(3), 205–229.
https://doi.org/10.1145/65943.65945
Rahman, T., Khandakar, A., Qiblawey, Y., Tahir, A., Kiranyaz, S., Abul Kashem, S. B., et al. (2021). Exploring the effect of image enhancement techniques on COVID-19 detection using chest x-ray images.
Computers in Biology and Medicine,
132, 104319. https://doi.org/
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compbiomed.2021.104319
Rai, A. (2020).
Explainable AI: from black box to glass box.
Journal of the Academy of Marketing Science,
48, 137–141.
https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s11747-019-00710-5
Riasi, A., Schwartz, Z., & Chen, C.-C. (2019). A paradigm shift in revenue management? The new landscape of hotel cancellation policies.
Journal of Revenue and Pricing Management,
18(6), 434–440.
https://doi.org/10.1057/s41272-019-00189-3
Ribeiro, M. T., Singh, S., & Guestrin, C. (2016a). "Why should I trust you?": Explaining the predictions of any classifier. In Proceedings of the 22nd ACM SIGKDD international conference on knowledge discovery and data mining, KDD san francisco, CA (pp. 1135–1144). New York, NY: Association for Computing Machinery.
Ribeiro, M. T., Singh, S., & Guestrin, C. (2016b).
"Why Should I Trust You?": Explaining the Predictions of Any Classifier. In
Proceedings of the 22nd ACM SIGKDD international conference on knowledge discovery and data mining, san francisco, CA, USA, august 13-17, 2016 (pp. 1135–1144).
https://doi.org/10.18653/v1/n16-3020
Ruder, S. (2017). An overview of multi-task learning in deep neural networks.
https://arxiv.org/abs/1706.05098
Rudin, C., Chen, C., Chen, Z., Huang, H., Semenova, L., & Zhong, C. (2021). Interpretable machine learning: Fundamental principles and 10 grand challenges. arXiv preprint arXiv:2103.11251.
Saarela, M., & Jauhiainen, S. (2021). Comparison of feature importance measures as explanations for classification models.
SN Applied Sciences,
3(2).
https://doi.org/10.1007/s42452-021-04148-9
Saito, T., & Rehmsmeier, M. (2015). The precision-recall plot is more informative than the ROC plot when evaluating binary classifiers on imbalanced datasets.
Plos One,
10(3).
https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0118432
Sánchez-Medina, A. J., & C-Sánchez, E. (2020). Using machine learning and big data for efficient forecasting of hotel booking cancellations.
International Journal of Hospitality Management,
89, 102546.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhm.2020.102546
Sandfort, V., Yan, K., Pickhardt, P. J., & Summers, R. M. (2019). Data augmentation using generative adversarial networks (CycleGAN) to improve generalizability in CT segmentation tasks. Scientific reports, 9(1), 1–9.
Semenova, L., Rudin, C., & Parr, R. (2019). A study in rashomon curves and volumes: A new perspective on generalization and model simplicity in machine learning. arXiv preprint arXiv:1908.01755.
Smith, S. J., Parsa, H. G., Bujisic, M., & van der Rest, J.-P. (2015). Hotel cancelation policies, distributive and procedural fairness, and consumer patronage: A study of the lodging industry.
Journal of Travel & Tourism Marketing,
32, 886–906.
https://doi.org/10.1080/10548408.2015.1063864
Staniak, M., & Biecek, P. (2018). Explanations of model predictions with live and breakDown packages.
Suzuki, K. (2017). Overview of deep learning in medical imaging. Radiological physics and technology, 10(3), 257–273.
Tang, F., Xiao, C., Wang, F., & Zhou, J. (2018). Predictive modeling in urgent care: A comparative study of machine learning approaches. Jamia Open, 1(1), 87–98.
Tatman, R., VanderPlas, J., & Dane, S. (2018). A practical taxonomy of reproducibility for machine learning research.
Thompson, N. C., Greenewald, K., Lee, K., & Manso, G. F. (2020). The computational limits of deep learning. arXiv preprint arXiv:2007.05558.
Tonekaboni, S., Joshi, S., McCradden, M. D., & Goldenberg, A. (2019).
What Clinicians Want: Contextualizing Explainable Machine Learning for Clinical End Use.
Machine Learning for Healthcare.
http://proceedings.mlr.press/v106/tonekaboni19a.html
Ucar, F., & Korkmaz, D. (2020). COVIDiagnosis-net: Deep bayes-SqueezeNet based diagnosis of the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) from x-ray images. Medical Hypotheses, 140, 109761–109761.
Vandewalle, P., Kovacevic, J., & Vetterli, M. (2009). Reproducible research in signal processing. IEEE Signal Processing Magazine, 26(3), 37–47.
Vanschoren, J., Rijn, J. N. van, Bischl, B., & Torgo, L. (2013). OpenML: Networked science in machine learning.
SIGKDD Explorations,
15(2), 49–60.
https://doi.org/10.1145/2641190.2641198
Varma, A., Sarma, A., Doshi, S., & Nair, R. (2018). House price prediction using machine learning and neural networks, 1936–1939.
https://doi.org/10.1109/ICICCT.2018.8473231
Vaswani, A., Shazeer, N., Parmar, N., Uszkoreit, J., Jones, L., Gomez, A. N., et al. (2017). Attention is all you need. arXiv preprint arXiv:1706.03762.
Wang, J., Li, M., Hu, Y., & Zhu, Y. (2009).
Comparison of hospital charge prediction models for gastric cancer patients: neural network vs. decision tree models.
BMC Health Services Research,
9(1).
https://doi.org/10.1186/1472-6963-9-161
Wang, L., Lin, Z. Q., & Wong, A. (2020a). COVID-net: A tailored deep convolutional neural network design for detection of COVID-19 cases from chest x-ray images.
Scientific Reports,
10(1), 19549.
https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-020-76550-z
Wang, L., Lin, Z. Q., & Wong, A. (2020b). COVID-net: A tailored deep convolutional neural network design for detection of COVID-19 cases from chest x-ray images.
Scientific Reports,
10(1), 19549.
https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-020-76550-z
Wang, R., Wang, X., & Inouye, D. I. (2021).
Shapley Explanation Networks.
ICLR.
https://openreview.net/forum?id=vsU0efpivw
Wang, S., Zha, Y., Li, W., Wu, Q., Li, X., Niu, M., et al. (2020). A fully automatic deep learning system for COVID-19 diagnostic and prognostic analysis.
European Respiratory Journal,
56(2).
https://doi.org/10.1183/13993003.00775-2020
Wiens, J., Guttag, J., & Horvitz, E. (2014).
A study in transfer learning: leveraging data from multiple hospitals to enhance hospital-specific predictions.
Journal of the American Medical Informatics Association,
21(4), 699–706.
https://doi.org/10.1136/amiajnl-2013-002162
Wiśniewski, J., & Biecek, P. (2021).
fairmodels: A Flexible Tool For Bias Detection, Visualization, And Mitigation.
arXiv:2104.00507.
https://arxiv.org/abs/2104.00507
Wright, M. N., & Ziegler, A. (2016).
XGBoost: A Scalable Tree Boosting System.
SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining.
https://doi.org/10.1145/2939672.2939785
Wright, M. N., & Ziegler, A. (2017).
ranger: A Fast Implementation of Random Forests for High Dimensional Data in C++ and R.
Journal of Statistical Software,
77(1), 1–17.
https://doi.org/10.18637/jss.v077.i01
WUoT. (2020). ML case studies: Reproducibility of scientific papers.
https://mini-pw.github.io/2020L-WB-Book/reproducibility.html
Yan, L., Zhang, H.-T., Goncalves, J., Xiao, Y., Wang, M., Guo, Y., et al. (2020a).
An interpretable mortality prediction model for COVID-19 patients.
Nature Machine Intelligence,
2(5), 283–288.
https://doi.org/10.1038/s42256-020-0180-7
Yan, L., Zhang, H.-T., Goncalves, J., Xiao, Y., Wang, M., Guo, Y., et al. (2020b).
An interpretable mortality prediction model for COVID-19 patients.
Nature Machine Intelligence,
2(5), 283--288.
https://www.nature.com/articles/s42256-020-0180-7
Yan, L., Zhang, H.-T., Goncalves, J., Xiao, Y., Wang, M., Guo, Y., et al. (2020c).
An interpretable mortality prediction model for COVID-19 patients.
Nature Machine Intelligence,
2(5), 283--288.
https://www.nature.com/articles/s42256-020-0180-7
Yildiz, B., Hung, H., Krijthe, J. H., Liem, C. C. S., Loog, M., Migut, G., et al. (2021). ReproducedPapers.org: Openly teaching and structuring machine learning reproducibility. In B. Kerautret, M. Colom, A. Krähenbühl, D. Lopresti, P. Monasse, & H. Talbot (Eds.), Reproducible research in pattern recognition (pp. 3–11). Cham: Springer International Publishing.
Zaimi Aldo, W. M., Herman, V., Antonsanti, P.-L., Perone, C. S., & Cohen-Adad, J. (2018). AxonDeepSeg: Automatic axon and myelin segmentation from microscopy data using convolutional neural networks.
Scientific Reports,
8(1), 3816.
https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-018-22181-4
Zhao, Q., Meng, M., Kumar, R., Wu, Y., Huang, J., Deng, Y., et al. (2020).
Lymphopenia is associated with severe coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) infections: A systemic review and meta-analysis.
International Journal of Infectious Diseases,
96, 131–135.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijid.2020.04.086
Zhao, Y., Chetty, G., & Tran, D. (2019). Deep learning with XGBoost for real estate appraisal, 1396–1401.
https://doi.org/10.1109/SSCI44817.2019.9002790
Zheng, Y., Zhu, Y., Ji, M., Wang, R., Liu, X., Zhang, M., et al. (2020a).
A Learning-Based Model to Evaluate Hospitalization Priority in COVID-19 Pandemics.
Patterns,
1(6), 100092.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.patter.2020.100092
Zheng, Y., Zhu, Y., Ji, M., Wang, R., Liu, X., Zhang, M., et al. (2020b).
A Learning-Based Model to Evaluate Hospitalization Priority in COVID-19 Pandemics.
Patterns,
1(9), 100173.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.patter.2020.100173
Zhou, Z.-H., & Feng, J. (2017). Deep forest: Towards an alternative to deep neural networks.
CoRR,
abs/1702.08835.
http://arxiv.org/abs/1702.08835
Zhou, Z., Siddiquee, M. M. R., Tajbakhsh, N., & Liang, J. (2019). UNet++: Redesigning skip connections to exploit multiscale features in image segmentation. IEEE Transactions on Medical Imaging.